Automatic translation
Everything you need to know about real-time machine translation.
How do global enterprises offer customer service in several languages? Sure, hiring an entire team of native speakers for each target language is one option — but that’s definitely not the most feasible approach and is not worth the time, effort and training. Meet integrated automatic translation.
Many businesses rely on automatic translation technology which produces instant and accurate translations. But you may wonder about the quality of the translations. And there are so many different translation solutions out there. How do you find the best one for your business?
Don’t worry, we’ve got the answers to all your questions.
Table of Contents
What is automatic translation?
Automatic translation, also known as machine translation, uses computer software to translate text from one language to another without human involvement.
The aim of machine translation is to provide comprehensible and linguistically accurate translations in real time. This is accomplished with machine translation engines which use AI.
Automated vs. automatic vs. machine translation: What’s the difference? Which one is real-time translation?
You might hear automatic translation and automated translation used interchangeably. There might be subtle nuances, but in several contexts, they both refer to the same thing: machine translation.
If you still want to get specific:
Automatic translation is exactly the same as machine translation. It translates text from one language to another automatically, without human intervention in the translation process.
Automated translation might be used to mean not only the translation process itself but also any other automation workflows, like pre-processing and post-processing tasks associated with translation.
Machine translation works to produce understandable and accurate translations in real time. That’s why it’s the best solution when you need to eliminate language barriers for instant communication.
How does machine translation work?
Rule-based machine translation
To answer this clearly, we need to take you on a short journey through history.
There are three approaches to machine translation. The first is Rule-based machine translation.
The earliest version of machine translation was built on hard-coded linguistic rules. In other words, this involved the rules of the source and target languages being manually written.
Rule-based machine translation isn’t scalable, because it takes a lot of time and effort.
Statistical machine translation
The faster translation tools of more recent times (like the kind Google Translate gives you) use enormous volumes of data from both the source and target languages to deliver the most probable translation. As the name implies, this approach analyzes the statistical relationships between the original words and their human translations to find the closest translation of the input text.
Statistical machine translation translates word by word, phrase by phrase or based on syntax. It can’t give you the most accurate translations because it doesn’t take the context into account. Not only that, this process is especially not suitable if you’re translating between two languages with differences in word orders (English to Chinese, for example),

Given the fluidity and complexity of human language, you can imagine the size of the datasets needed to train these systems: We’re talking at least 2 million words. This makes it an incredibly time-consuming and costly process, and it definitely doesn’t give you the most accurate and context-aware translations you need for business communication.
Neural machine translation (NMT)
Neural machine translation (NMT) is the latest evolution of machine translation.
Just like statistical machine translation, NMT is data-driven. The biggest difference is that NMT takes this several steps further: It leverages large artificial neural networks, such as transformers and recurrent neural networks (RNNs), to predict the likelihood of correct translations as well as continuously improve the accuracy of real-time translations.
The language models for NMT are built and improved through an iterative training process that involves exposure to millions of sentence-specific translations between language pairs, gradually adjusting its output to identify and minimize translation errors over time.
In other words, NMT isn’t just trained on individual words or phrases and their translations: It’s trained on clusters of related words and words with similar meanings. You might find a word that has multiple meanings simultaneously appearing in different clusters.
That’s how you get the most accurate translation for a word in that context. Depending on the context, NMT would associate the word “bark” with dog, tree or a beloved chocolate recipe, and instantly return the correct translation.
When to use automatic machine translation

eCommerce
Machine translation is the most appropriate solution for several use cases. Here are a few pertinent ones in business.
Product listings, descriptions and reviews are all great candidates for automatic translation. This helps ecommerce companies expand globally and market their products to an international audience.
Documentation
Automatic translation is able to handle large volumes of text and efficiently and quickly generate translations. This makes it a valuable resource to translate various types of documents, including instruction manuals and help center and support documentation.
Customer service
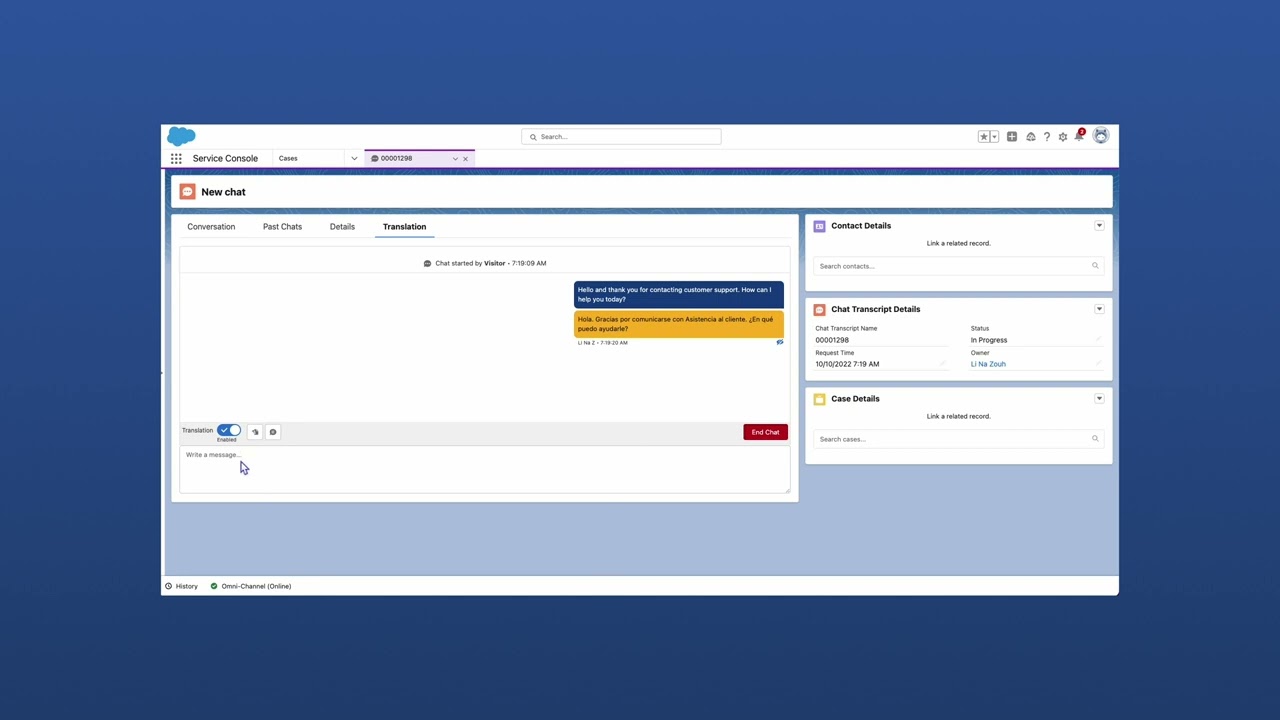
With machine translation, support agents can respond to customer queries instantly. Since this is a time-sensitive use case which needs natural language response with empathy, automatic translation is one of the best ways to get real-time translations and address customer queries accurately.
Customer service machine translation successfully enables complete communication: It accurately translates customer requests as well as agent responses.
NMT-based solutions designed just for this purpose and trained with data specific to your subject matter and domain, like Language I/O, would integrate directly with email, live chat or chatbot platforms and enable brands to communicate with their customers all over the world in any language. Not only that, it would also help your customer service team scale operations and improve customer experience across different channels without the need to hire more employees with language skills.
Accuracy and quality
What is the accuracy and quality of machine translation?
The accuracy and quality of machine translation depends on several factors, including
- the machine translation engine or technology
- the source and target languages (also known as language pair)
- training data
NMT is the most advanced and universally seen as the most versatile and accurate machine translation solution.
The greatest advantage of neural machine translation is that it improves with every translation. The more translations for a specific language or domain it performs, the higher the quality and speed of the output. It also becomes easier to keep adding more languages.
What are the benefits of automatic translation?

Efficiency
Automatic translation comes with great accuracy, speed and versatility, which makes it an invaluable tool with a great many benefits, especially for global businesses.
Machine translation can analyze and translate large volumes of text rapidly, saving plenty of time and resources. Compare this to manual translation, which leaves humans with repetitive tasks that take a great deal of time and effort. Machine translation takes routine translation tasks off the table, handling them quickly and efficiently, allowing humans to focus on more complex problems.
Cost-effectiveness
Machine translation significantly reduces translation costs. Enterprises with high volumes of translation needs can eliminate the need to hire employees for every task and language and automate the translation process, which results in increased operational efficiency and cost savings.
Speed
Machine translation provides accurate real-time translations, enabling fast communication. This is advantageous especially in time-sensitive scenarios which may also require high precision, like customer service or social media.
Scalability
Automatic translation technology is highly scalable and can handle both small- and large-scale translation projects of varying complexities. It’s easy to add more languages to machine translation and make changes in translation volumes or requirements, making it highly versatile and adaptable. This also helps companies expand globally without necessarily having to hire people in different countries.
Customization
Many advanced machine translation solutions, like Language I/O, offer a variety of customization options that enable brands to get highly tailored translations. Depending on the domain, industry or preferences, machine translation models can be fine-tuned for factors like voice, tone and terminology.
Languages
Instead of taking the time hiring employees who can translate in multiple languages, businesses can get started translating between a large number of language pairs right away. With more sophisticated machine translation solutions like Language I/O, it’s possible to start translating in more than 150+ languages in less than 24 hours.
Accessibility and global communication
Automatic translation makes it possible to communicate and share information across borders and without language barriers. This promotes diversity, inclusivity and accessibility, and powers global trade and collaboration across cultures and languages.
Automatic translation for customer support
Apart from the above benefits, machine translation technology has other features that make it the perfect solution for automating customer service in multiple languages. Here are a few support-specific attributes that competitive machine translation solutions like Language I/O have.
Security-first approach
In most cases, customer service involves deeply sensitive customer data and personally identifiable information such as credit card number, driver’s license, contact details, etc. If support agents paste such highly critical private data into open-source translators or other free solutions, it puts the company at risk of data breaches, noncompliance with global privacy regulations and cyberthreats like phishing, and ultimately, damage the brand reputation. That’s why it’s crucial to use a customer service machine translation solution that prioritizes security and protects your customers’ data.
For example, Language I/O automatically masks all personally identifiable data before even translating any content. After the real-time translation is complete, all data is completely erased from all the systems and nothing is retained.
Multi-engine machine translation
Different machine translation engines are better trained in different domains. Some high-end machine translation platforms, like Language I/O, evaluate multiple engines and pick the most appropriate translation engine for the translation requirement.
In multi-engine machine translation, the same input is sent to multiple engines. The translations are then compared for accuracy and quality, and the best one is then served as the output. With time and training, the platform automatically selects the best engine for the job and gives you consistently higher quality translations than a single engine could achieve.
Integration
An external machine translation solution that leaves support agents juggling different windows and applications is highly inefficient and leads to a frustrating experience. To save time and make everyone’s life and work easier, you need an automatic translation solution that would be deeply embedded into the technology platforms you already use, like Salesforce or Zendesk.
Language I/O, for instance, comes with integrations to several CRM platforms as well as a flexible and secure API that would help teams connect to any of their preferred solutions.
Automatic translation for customer service channels

Machine translation is highly versatile. Aside from being integrated with the CRM platform of your choice, it can be adapted to translate any of your written customer service channels. Let’s look closely at these channels.
Live chat
Real-time chat translation enables support agents to quickly understand customer queries in any language and communicate instantly in the customer’s preferred language. The agent doesn’t need any language skill to make this happen: A machine translation platform like Language I/O acts as an instant chat translator, helping the agent translate live chat messages directly within the CRM or chat program to maintain existing workflows.
Email and ticket
While email and ticket are not channels that require real-time translation, machine translation makes it possible for agents to quickly power through a large number of customer service queries in multiple languages. For instance, Language I/O enables automatic translation right in the CRM where the agents answer the tickets, so they can maintain their workflows and processes.
Chatbot
Chatbot translation technology translates messages sent to and from a chatbot. This real-time chatbot translation enables customer service, sales, and marketing teams to quickly deploy chatbots that can communicate with customers and prospects in their preferred language, making for clear and accurate communication and improved experience.
FAQ and knowledge bases
Self-service options like knowledge bases, support articles and FAQ are available 24/7 and help customers find answers to their questions fast, without having to wait to be addressed. When translated, this highly efficient solution empowers customers to take control of their own support and independently find the right solutions, reducing ticket volumes and improving first-contact resolution across languages. Integrating a machine translation solution like Language I/O directly to your CRM eliminates extra steps to translate and localize articles and even automatically localizes site links for URL consistency across all languages.
Social media
Social media has increasingly become a critical customer service channel for timely customer service and crisis management. Businesses can capitalize on the reach social media has by using a machine translation solution that helps them instantly translate social media posts, address customer complaints quickly and engage with a global audience, which would give them a huge competitive advantage. Language I/O offers a browser plugin that enables businesses to use real-time machine translation on social media channels as well.